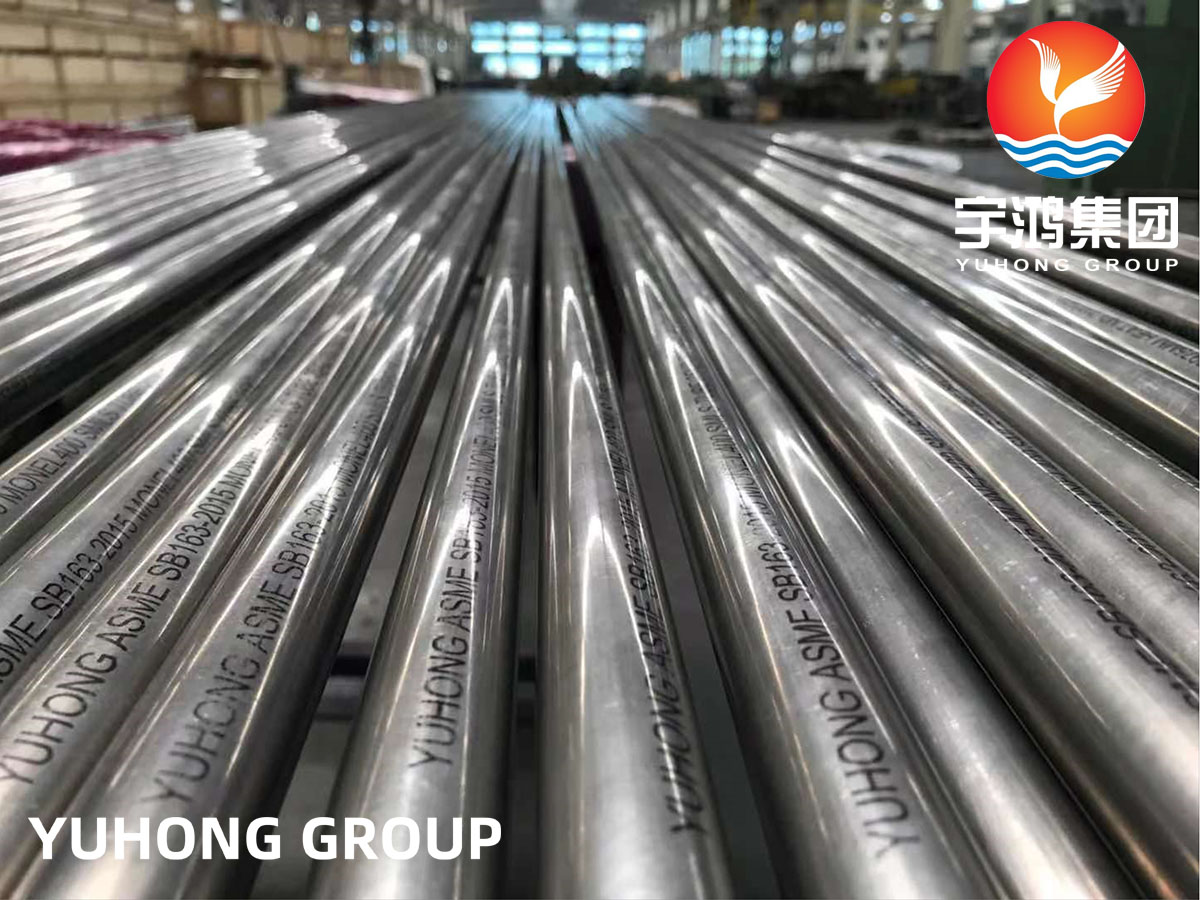
1. Impact of Pipe Thickness
Pressure Resistance: Thicker pipes can handle higher pressures without failing, making them suitable for high-pressure systems like oil pipelines and heat exchangers.
Strength: Thicker walls give the pipe more strength to resist bending, impacts, and external forces, which is important in demanding environments (e.g., industrial settings).
Thermal Insulation: Thicker pipes better retain heat, which is useful in high-temperature applications, but they can be more expensive and harder to work with.
Corrosion Resistance: Thicker walls provide more protection against corrosion, especially in harsh environments like seawater or chemical plants.
2. Impact of Pipe Diameter
Flow Capacity: Larger diameter pipes can carry more fluid, which is essential for systems with high flow rates (like cooling systems).
Structural Considerations: Larger pipes are heavier and can be more prone to deformation, so they need stronger support structures.
Flexibility: Larger pipes are harder to bend, making them more challenging to install in tight spaces.
Weight: Larger and thicker pipes are heavier, which can increase installation and transportation costs.
3. Combined Effect of Thickness and Diameter
Pressure and Flow: For high-pressure or high-temperature systems, both thicker walls and larger diameters are needed. Thicker walls resist pressure, while larger diameters allow more fluid to flow.
Cost vs. Benefit: Both thickness and diameter increase costs. Thicker pipes offer more durability and resistance to failure, while larger pipes boost flow capacity but are more expensive to produce and install.
Fatigue Resistance: Larger diameter pipes are more prone to stress from pressure changes, but thicker walls help resist this stress.

 English
English